Crohn’s Disease
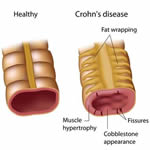 Crohn's Disease is a chronic condition that causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract. The inflammation often spreads deep into affected tissues and can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall, as depicted in the accompanying graphic.
Crohn's Disease is a chronic condition that causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract. The inflammation often spreads deep into affected tissues and can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall, as depicted in the accompanying graphic.
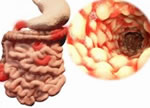 In Crohn’s Disease, inflammation can involve different areas of the digestive tract — anywhere from mouth to anus, although it is predominantly found in the small bowel. The inflammation of the intestine can “skip,” leaving normal areas in between patches of diseased intestine. The longer someone has Crohn's Disease, the more likely they will be impacted by penetrating disease, which can lead to strictures, obstructions and/or fistulas in the intestines.
In Crohn’s Disease, inflammation can involve different areas of the digestive tract — anywhere from mouth to anus, although it is predominantly found in the small bowel. The inflammation of the intestine can “skip,” leaving normal areas in between patches of diseased intestine. The longer someone has Crohn's Disease, the more likely they will be impacted by penetrating disease, which can lead to strictures, obstructions and/or fistulas in the intestines.
What Causes Crohn's Disease?
The exact cause of Crohn's Disease is unknown. Researchers believe the following factors may play a role in causing Crohn's Disease:
- Autoimmune reaction
- Genes
- Environment
The Autoimmune reaction: Scientists believe one cause of Crohn's Disease may be an autoimmune reaction—when a person's immune system attacks healthy cells in the body by mistake. Normally, the immune system protects the body from infection by identifying and destroying bacteria, viruses, and other potentially harmful foreign substances. Researchers believe bacteria or viruses can mistakenly trigger the immune system to attack the inner lining of the intestines. This immune system response causes the inflammation, leading to symptoms.
Genes: Crohn's Disease sometimes runs in families. Research has shown that people who have a parent or sibling with Crohn's Disease may be more likely to develop the disease. Researchers continue to study the link between genes and Crohn's Disease.
Environment: Some studies suggest that certain things in the environment may increase the chance of a person getting Crohn's Disease, although the overall chance is low. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and oral contraceptives may slightly increase the chance of developing Crohn's Disease. A high-fat diet may also slightly increase the chance of getting Crohn's Disease.
Some people incorrectly believe that eating certain foods, stress, or emotional distress can cause Crohn's Disease. Emotional distress and eating certain foods do not cause Crohn's Disease. Sometimes the stress of living with Crohn's Disease can make symptoms worse. Also, some people may find that certain foods can trigger or worsen their symptoms.
Who is at risk for Crohn's Disease? Crohn's Disease can occur in people of any age. However, it is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 20 and 29 who have a family member (most often a sibling or parent) with IBD who smoke cigarettes. It takes an average of 3 years from the onset of symptoms until diagnosis, and in some cases, it may take even longer.
Next Page: The Signs and Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease